Introduction
Have you or someone you know experienced chronic joint pain? It could be a sign of degenerative joint disease, also known as osteoarthritis. This condition affects millions of people globally and is one of the leading causes of disability in older adults. In this article, we will explore what degenerative joint disease is, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and related topics to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Understanding Degenerative Joint Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
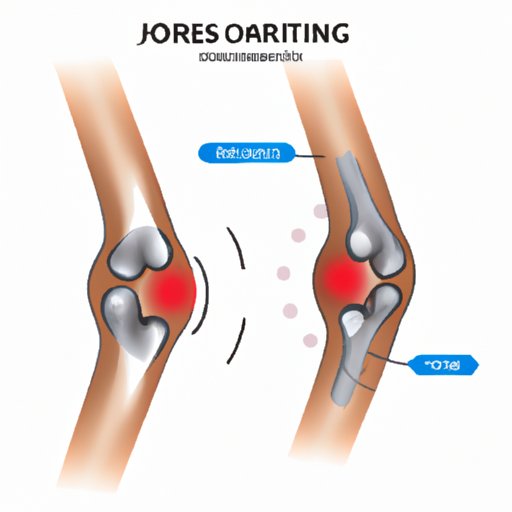
Degenerative joint disease (DJD) is a condition that affects the joints, especially those in the knees, hips, and spine. It is caused by the wear and tear of the cartilage cushioning the ends of the bone that forms the joint. As cartilage degenerates, the bone rubs against each other, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility.
Other causes of DJD include obesity, overuse injuries, joint injury or trauma, and genetic factors. Symptoms of DJD vary but often include joint pain, stiffness, tenderness, difficulty moving, clicking or cracking sounds, and bone spurs. Initially, symptoms may appear after strenuous exercise and gradually worsen over time.
Treatment options for DJD include medication, therapy, and surgery. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, and corticosteroid injections can reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and exercise can improve mobility and balance. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery or arthroscopy can reduce pain and improve joint function.
The Silent Enemy: A Comprehensive Guide to Degenerative Joint Disease
DJD is a progressive disease that develops silently over time. The early stages may not show symptoms, making it difficult to detect with just an x-ray. Over time, the cartilage wears away, and the bones start to rub against each other, leading to joint damage and deformity.
Other symptoms of DJD include weak muscles, reduced range of motion, and deformity. In some cases, the damage may require surgery to remove bone spurs or realign the joint. DJD can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and disability. Early detection and treatment are crucial to reducing its impact on daily life.
The Slow Progression of Degenerative Joint Disease and How to Manage Its Effects
DJD progresses slowly, and its impact on daily life varies. It affects people differently, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution for managing the condition. However, there are ways to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle changes such as weight loss, reducing stress on the joints, and regular exercise can help reduce pain and improve mobility. Stretching, joint-strengthening exercises, and aerobic activities like biking or swimming can reduce joint stiffness and improve muscle strength. Joined support devices like braces or canes can help relieve pressure on the joint and improve balance.
Degenerative Joint Disease: A Condition That Affects Millions, But Few Know About
DJD is one of the most prevalent forms of arthritis and affects millions globally. Yet, it often goes undiagnosed and untreated, making it a silent enemy for many older adults. This could be due to a lack of awareness, inadequate screening, or a reluctance to see a doctor due to stigma.
Early detection and treatment are crucial to preserving joint function and preventing further damage. Screening tests like x-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect early signs of DJD in the joints. Treatment options such as medication, lifestyle changes, and surgery can reduce pain and improve mobility and overall quality of life.
Living with Degenerative Joint Disease: Overcoming Pain and Disability
Living with DJD can be challenging, and it can have a significant impact on your emotional and mental well-being. It is crucial to seek emotional support and mental fortitude to overcome the pain and disability associated with this condition.
Practical tips for managing DJD include staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress on the joints, and engaging in activities that bring joy and purpose. It is also essential to stay connected with friends and family, seek professional support in coping with the condition, and stay positive and optimistic.
Degenerative Joint Disease: Aging’s Effect on the Body’s Most Essential Joints
Aging is one of the primary risk factors for developing DJD as our body’s joints become more brittle, less flexible, and susceptible to injury with age. Bones become less dense and weak, and joints become less flexible due to the loss of cartilage. This makes older adults more vulnerable to joint damage and disease.
Actions that can be taken to slow down the degenerative process include staying active, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and wearing protective gear when engaging in high-risk activities. These measures can help reduce the risk of falls, fractures, and joint injury, and protect against other age-related conditions.
Exploring the Science of Degenerative Joint Disease: A Look into the Latest Research and Discoveries
There have been many recent advances in our understanding of DJD. The latest research has been focused on finding novel treatment methods and improving our understanding of the disease’s biology and mechanisms.
Some promising treatments include stem cell therapy, platelet-rich plasma injections, and gene therapy. These new treatments can reduce inflammation, promote the growth of new cartilage, and improve joint function. Clinical trials are ongoing, and more research is necessary to determine their effectiveness and safety fully.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DJD is a common condition that affects millions worldwide and is one of the leading causes of disability in older adults. While it is a silent enemy and progresses slowly, early detection and treatment are essential to reducing its impact on daily life. Lifestyle changes, medication, therapy, and surgery are some of the treatment options available. Keeping a positive attitude, seeking emotional support, and staying active are crucial in managing DJD and overcoming pain and disability.





