I. Introduction
Physical maps are an essential tool for anyone interested in understanding the Earth’s geography. Whether you’re a student, a geography enthusiast, or simply interested in exploring the world around you, physical maps can provide valuable insights into the natural world.
II. Exploring the World through Physical Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
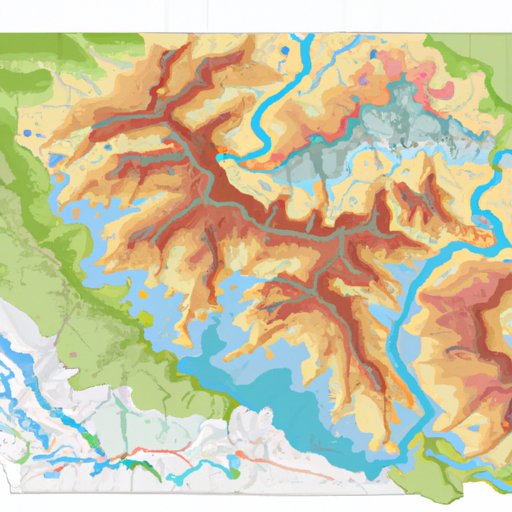
Physical maps are maps that provide information about the physical features of the Earth’s surface. These features include topography, land use, climate, and other natural characteristics. Physical maps are typically drawn at a relatively large scale, because they show detailed information about the Earth’s surface.
Physical maps include a variety of information, including topography, which shows the shape and elevation of the land; land use, which shows how the land is being used (for example, agriculture, forest, urban areas); and climate, which shows the patterns of temperature, precipitation, and other weather conditions.
Tips and tricks for interpreting physical maps include understanding the legend, or key, which explains the symbols used on the map; understanding how to read contour lines, which show the shape of the land; and being aware of projection, which is the process of transforming a three-dimensional globe onto a two-dimensional surface.
Key differences between physical maps and other types of maps include political maps, which show the boundaries and features of countries and states; and thematic maps, which show a particular theme or topic, such as population density, natural resources, or climate zones.
III. Why Physical Maps are Important for Understanding the Earth’s Geography
Physical maps are important for understanding the natural world and the interactions between different physical features. They provide a visual representation of these features, which can help people better understand the world around them.
Information provided by physical maps includes the distribution of flora and fauna, the location of different landforms, and the relationships between natural and human-made features. This information is essential for anyone interested in understanding Earth’s geography, including scientists, researchers, and policy-makers.
IV. Making Sense of Physical Maps: A Beginner’s Guide
For beginners, physical maps can be intimidating and difficult to understand. However, there are several key things to keep in mind when interpreting physical maps.
The first step is to become familiar with the legend or key, which explains what the different symbols and colors on the map represent. Contour lines, which show the shape of the land, can also be difficult to understand at first. However, with practice, readers can learn to interpret the shape and distance between contour lines to understand the shape of the land.
Visual examples and practical exercises can be helpful for beginners to develop their map-reading skills. For example, studying a topographic map of a familiar area, such as a local park, can help readers understand how to read contour lines and interpret topography.
V. Physical Maps vs. Political Maps: What’s the Difference?
Physical maps and political maps provide different types of information about the Earth’s surface. Political maps show boundaries and features of countries and states, including cities, roads, and political boundaries. Physical maps, on the other hand, show the natural features of the Earth’s surface, including topography, land use, and climate.
While political maps are important for understanding political boundaries and features, physical maps are essential for understanding the natural world and the interactions between different features.
VI. The Changing Face of Physical Maps: How Technology is Advancing Mapmaking
New technologies are advancing the field of mapmaking, which is allowing mapmakers to create more detailed and accurate maps of the Earth’s surface. One of the most significant advancements is LiDAR, which uses laser light to measure the distance between the Earth’s surface and the mapping instrument. Sensitive sensors and advanced imaging techniques are used to create detailed images of the Earth’s surface.
Remote sensing is another technology that is being used to create more detailed and accurate physical maps. This technology uses satellite imagery and other remote sensing techniques to collect data about the Earth’s surface. This data is then used to create detailed maps and models of the Earth’s surface.
VII. Conclusion
Physical maps are an essential tool for anyone interested in understanding the natural world. In this comprehensive guide, we have covered the definition and explanation of physical maps, the information shown on physical maps, tips and tricks for interpreting physical maps, the importance of physical maps, a beginner’s guide to physical maps, a comparison of physical and political maps, and advancements in mapmaking technology.
We hope that this guide has been informative and helpful for readers interested in exploring the world through physical maps. We encourage readers to continue learning about physical maps and their importance in understanding the world around us.





