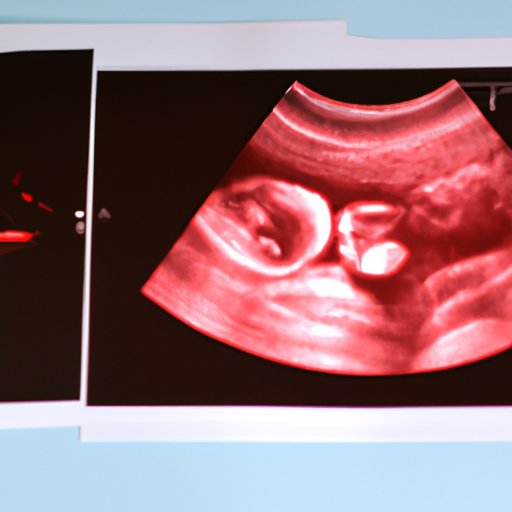
Introduction
Ultrasound, a non-invasive diagnostic tool, has revolutionized the field of obstetrics and gynecology. One of the key features of an ultrasound exam during pregnancy is locating the placenta. The placenta is a vital organ responsible for sustaining the growing fetus by ensuring adequate nourishment and oxygen supply. Hence, identifying its location is crucial for monitoring the health of the pregnancy. In this article, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to locate the placenta on ultrasound, things to avoid, and what to do in case of complications.
Understanding the Placenta
The placenta is an organ attached to the inner lining of the uterus that develops during pregnancy. It’s formed from the cells of the fertilized egg that divide to form the blastocyst. By the end of the first trimester, it’s fully formed and starts functioning. Its primary role is to act as a mediator between the mother and fetus by supplying oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products. It also produces hormones that play a vital role in maintaining a pregnancy.
The placenta is not a static organ as its location in the uterus changes as pregnancy progresses. The three parts of the placenta include the “chorion,” the outermost layer that forms from the trophoblast, the “amnion,” the innermost membrane that encloses the fetus, and the placental disk, the part of the placenta where exchange of nutrients and waste occurs.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Locate the Placenta on Ultrasound
Let us go through the steps that will help in identifying the placenta:
Step 1: Checking the gestational age
Before starting with the ultrasound, it’s crucial to check the gestational age as the location of the placenta depends on it. It’s easier to locate the placenta in the second or third trimesters as it’s comparatively larger and well-formed than in the first trimester.
Step 2: Identifying the uterus
The first step is to identify the uterus by sweeping the ultrasound probe over the lower abdomen. You can identify the uterus by recognizing the gestational sac, a fluid-filled structure that contains the developing fetus.
Step 3: Locating the fetal pole
The next step in locating the placenta is to identify the fetal pole, the early stage of fetal development. It’s characterized by a small white dot located adjacent to the gestational sac. The fetal pole helps in determining the location of the uterus and gestational age.
Step 4: Identifying the amniotic fluid
Once the fetal pole has been located, the next step is to identify the amniotic fluid. It’s a clear, straw-colored fluid that fills the amniotic sac, a membrane that encloses the fetus. The amniotic fluid is crucial for fetal development, as it helps cushion the fetus and allows for free movement.
Step 5: Locating the placenta
The last step in locating the placenta is to identify a round or oval-shaped structure on the side of the uterus. It may have a lobulated appearance or even be irregularly shaped. It’s usually located in the upper part of the uterus. Once you identify the placenta, you can determine its relationship to the fetus.
Visual Aids
Using visual aids can make it easier to understand the location of the placenta. Here are some visual aids that can help you:
Diagrams showing placenta positioning
There are many diagrams available that illustrate various positions of the placenta in the uterus. These diagrams are used as educational tools during the ultrasound examination and can help you to visualize the location of the placenta.
Videos demonstrating how to locate the placenta
Many videos are available online that show how to locate the placenta on ultrasound. These videos are created by medical professionals and can be helpful in understanding the process of locating the placenta.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Identifying the placenta on ultrasound requires skill and experience. Here are some of the common mistakes that should be avoided:
Misidentifying other structures as the placenta
The ultrasound exam produces many different structures and patterns on the screen, which can sometimes be misleading. Therefore, it’s important to recognize the specific characteristics of the placenta.
Errors in interpretation
Interpreting the ultrasound images correctly can be challenging. It’s important to take into consideration the gestational age and other factors such as the position of the baby and the amount of amniotic fluid.
Tips to avoid misidentification
Following tips should be kept in mind to avoid misidentification:
- It’s important to understand the characteristics of the placenta and its features so that it can be identified correctly on the ultrasound.
- Utilizing different ultrasound views or techniques, such as transabdominal or transvaginal, can be helpful in locating the placenta.
- Seeking the opinion of an experienced specialist if there is any doubt can be beneficial.
Normal vs. Abnormal Location
In most cases, the location of the placenta is entirely normal and does not cause any complications. However, sometimes the placenta can be abnormally positioned in the uterus, leading to complications. Some of the danger signs that indicate abnormal positioning include:
- Placenta previa, a condition where the placenta covers the cervix.
- Placenta accreta, where the placenta grows too deep into the wall of the uterus.
- Placenta increta, where the placenta grows into the muscles of the uterus.
- Placenta percreta, where the placenta grows through the uterus and into other organs, such as the bladder.
These complications can lead to severe bleeding during pregnancy and delivery and may require special care during labor. If any of these complications are suspected, it’s essential to consult an obstetrician and a specialist in maternal-fetal medicine.
When Further Testing is Necessary
In some cases, further imaging may be necessary to evaluate the position of the placenta accurately. These tests may include:
- MRI scan, which provides detailed information about the location and attachment of the placenta.
- Color Doppler ultrasound, which shows the blood flow in the placenta and adjacent tissues.
- Transvaginal ultrasound, which provides a more detailed view of the uterus and the placenta than transabdominal ultrasound.
Multiple Perspectives
Locating the placenta requires a team approach involving obstetricians, radiologists, and other specialists. In some cases, multiple perspectives and opinions can be helpful. Here are some perspectives from different specialists:
- An obstetrician views the placenta as a crucial organ that is responsible for the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus. They play a critical role in providing prenatal care and monitoring throughout pregnancy.
- A radiologist views the placenta as an image produced by an ultrasound machine. They have the expertise in interpreting these images and providing accurate information about the location and health of the placenta.
- A maternal-fetal medicine specialist views the placenta as a complex organ that requires special care and attention. They have the expertise to diagnose and treat complex cases, such as placenta previa and placenta accreta.
Conclusion
The placenta is a vital organ that plays an essential role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Accurately locating the placenta on ultrasound is crucial to monitor its position and function. A step-by-step guide, along with visual aids, can help in identifying the placenta on the ultrasound. Avoiding common mistakes and understanding the potential dangers associated with abnormal positioning of the placenta is important. If any concerns or complications arise during the ultrasound exam, it’s important to consult with an obstetrician or specialist.





